Nutrients Against Noise?
What’s this I hear about vitamins to protect against hearing loss? True?
Andrew Weil, M.D. | May 1, 2007

Maybe so, but we won’t know for sure until researchers confirm that what they’ve seen in animal studies holds up for humans. Here’s the story: investigators at the University of Michigan found that giving high doses of vitamins A, C and E plus magnesium to guinea pigs one hour before exposing them to excessive noise was protective. The noise was loud enough to induce hearing loss, and the vitamin and mineral doses were repeated once a day for five days. Hearing loss is associated with prolonged exposure to loud noises – jets taking off, guns firing, even the amplified sounds of music at rock concerts or from your iPod.
The Michigan researchers explained that noise-induced trauma causes the energy-producing mitochondria in the nerve cells of the ear to churn out damaging free radicals. In turn, excessive free radical activity can damage the inner ear leading to hearing loss. In their study they compared the effects of three combinations of the vitamins with magnesium and a placebo in guinea pigs. One group got vitamins A, C and E; another got A, C, and E plus magnesium; a third got magnesium alone and a fourth received placebos. All groups were then exposed to noise as loud as the sound of a jet taking off at close range. The researchers reported that the combination of vitamins A, C, E plus magnesium prevented the damage that leads to hearing loss, and hypothesized that the doses taken after noise exposure seem to have “scavenged” the free radicals that continue to form even after noise exposure ends.
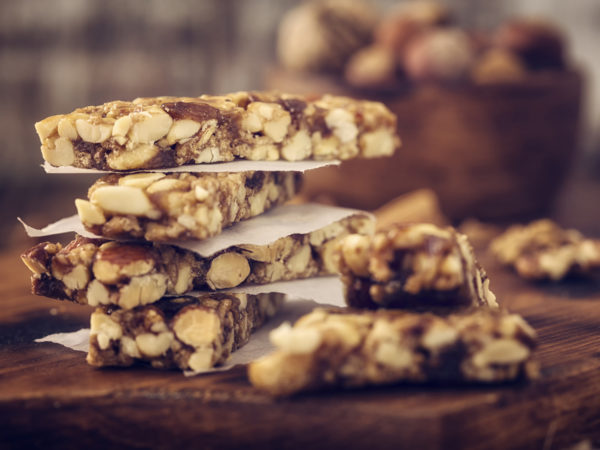
If this formula works as well in humans as it did in animals, the Michigan researchers said they envision combining the vitamins and magnesium into a nutrition bar to be given to soldiers for daily hearing protection in war zones. They also suggested that the nutrition bar could benefit people whose hearing is at risk because they work in noisy environments or frequently attend noisy events, or who habitually listen to loud music on their iPods. The Michigan study was published on February 20, 2007 online in the journal Free Radical Biology and Medicine.
The lead researcher is confident enough that the findings will hold up in humans to have launched a startup company to develop the vitamin/magnesium combination.
Andrew Weil, M.D.